Grazing management involves the strategic use of livestock to maintain and improve pasture health. Effective grazing practices enhance soil quality and biodiversity.
Grazing management is crucial for sustainable agriculture. It ensures optimal pasture utilization, preventing overgrazing and soil erosion. Livestock rotation and rest periods for pastures are essential techniques. These practices promote plant regrowth and maintain soil fertility. Healthy pastures result in better livestock health and productivity.
Grazing management also supports biodiversity by allowing various plant species to thrive. It reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, making it environmentally friendly. Implementing effective grazing strategies requires knowledge of local climate, soil types, and pasture species. Sustainable grazing benefits farmers, livestock, and the environment.
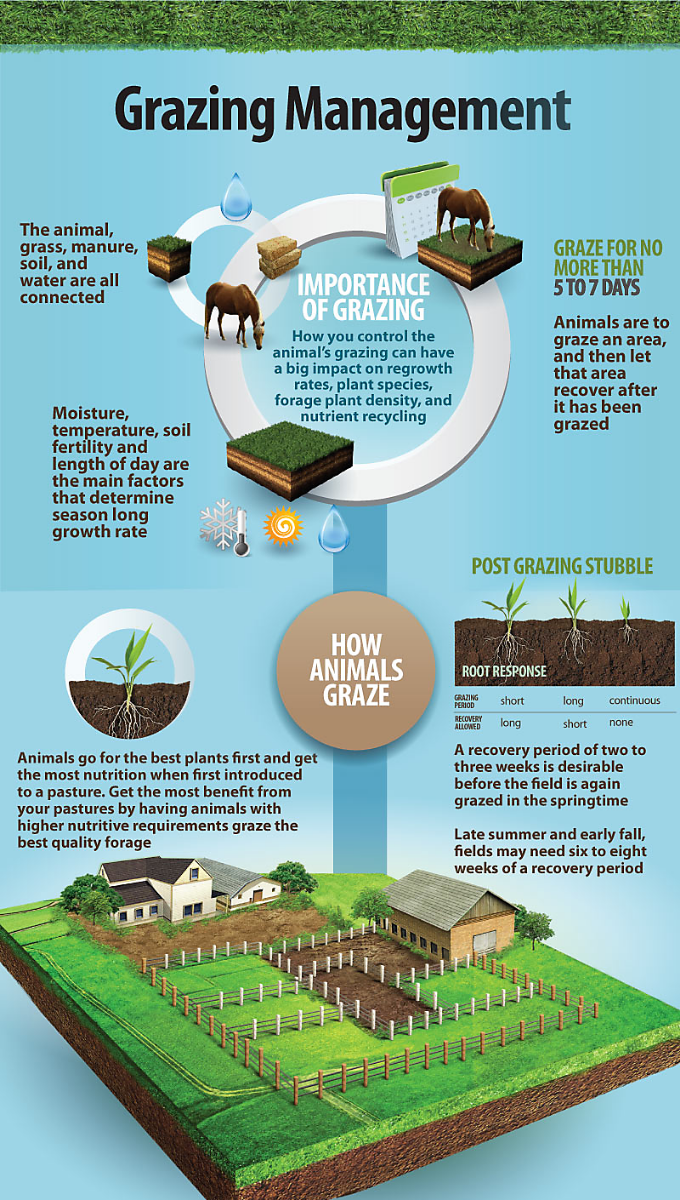
Importance Of Grazing
Grazing management is key to maintaining healthy pastures. Proper grazing helps the land, animals, and plants thrive. Understanding the importance of grazing can lead to better practices. This helps in achieving sustainable agriculture and preserving the environment.
Benefits For Soil Health
Grazing has many benefits for soil health. Healthy soil is crucial for growing plants and sustaining ecosystems. Grazing animals help in breaking down plant material. This process returns nutrients to the soil.
Improved soil structure is another benefit. Grazing animals' hooves press plant matter into the soil. This helps improve soil aeration and water infiltration. Proper grazing management also reduces soil erosion. This keeps the soil where it belongs.
- Enhanced nutrient cycling
- Improved water retention
- Reduction in soil compaction
Grazing also promotes root growth. Plants with stronger roots hold the soil better. This reduces erosion and improves soil stability. Proper grazing practices are essential for maintaining soil health.
Impact On Biodiversity
Grazing impacts biodiversity in both positive and negative ways. Properly managed grazing can increase plant species diversity. This creates a healthier ecosystem. Different plant species provide a variety of food sources for animals. This supports a diverse range of wildlife.
Overgrazing, however, can harm biodiversity. It can lead to the dominance of certain plant species. This reduces the variety of plants and animals in the area. Balanced grazing helps maintain a variety of plant species. This, in turn, supports a diverse animal population.
| Positive Impacts | Negative Impacts |
|---|---|
| Increased plant diversity | Reduction in plant variety |
| Support for various wildlife | Harm to certain species |
| Healthier ecosystems | Soil degradation |
Grazing management is key to ensuring a positive impact on biodiversity. This includes controlling the number of animals and the duration of grazing. Sustainable practices help in preserving the environment for future generations.
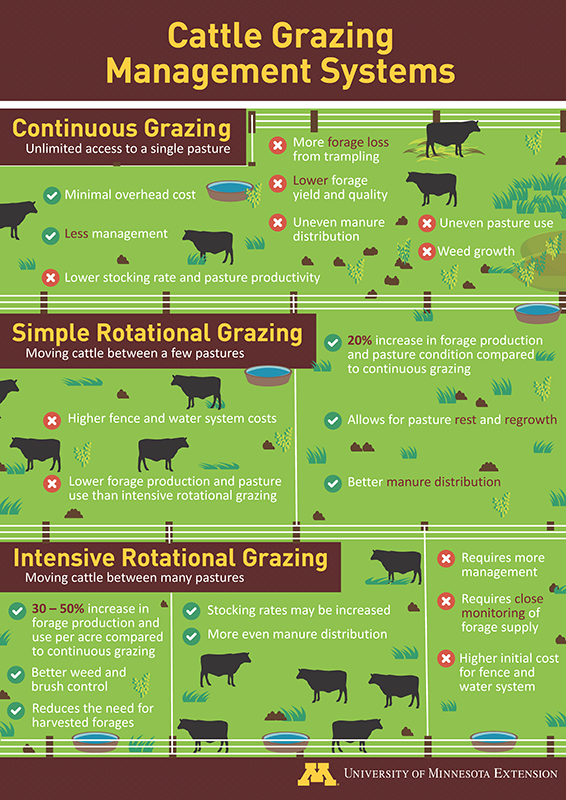
Types Of Grazing Systems
Grazing management is a critical aspect of sustainable agriculture. It involves the strategic use of livestock to manage pasture resources. Different grazing systems can optimize forage use, improve soil health, and increase livestock productivity. This blog post will explore two main types of grazing systems: Continuous Grazing and Rotational Grazing.
Continuous Grazing
Continuous Grazing allows livestock to graze in a specific area for an extended period. This system is simple and requires minimal management. However, it can lead to overgrazing in some areas while others are underutilized.
Advantages of Continuous Grazing:
- Low management effort
- Simple to implement
- Reduced fencing costs
Disadvantages of Continuous Grazing:
- Overgrazing can occur
- Uneven forage utilization
- Soil health may decline
Continuous Grazing works best in low-intensity farming operations. It is suitable for areas where pasture growth is uniform throughout the year. Farmers must monitor forage availability closely to avoid overgrazing.
Rotational Grazing
Rotational Grazing involves dividing pasture into smaller paddocks. Livestock are moved between these paddocks regularly. This system allows pastures to rest and recover, leading to better forage growth and soil health.
Advantages of Rotational Grazing:
- Improved forage utilization
- Enhanced soil health
- Increased livestock productivity
Disadvantages of Rotational Grazing:
- Higher management effort
- Increased fencing costs
- Requires careful planning
Rotational Grazing can significantly improve pasture productivity. It is ideal for high-intensity farming where maximizing forage use is critical. Farmers need to plan grazing schedules and monitor pasture conditions to achieve the best results.
Grazing Techniques
Grazing management is essential for maintaining healthy pastures and livestock. Different grazing techniques can help achieve these goals. These techniques aim to optimize pasture use and improve animal health. Two popular methods are strip grazing and mob grazing.
Strip Grazing
Strip grazing involves dividing a pasture into smaller strips. Animals graze each strip for a short period. This method helps control the grazing intensity. It ensures that the pasture is not overgrazed.
Benefits of strip grazing include:
- Better pasture utilization: Animals graze more evenly.
- Reduced waste: Less trampling and soil compaction.
- Improved regrowth: Pasture gets time to recover.
Here is a comparison of continuous grazing and strip grazing:
| Continuous Grazing | Strip Grazing |
|---|---|
| Animals graze freely. | Animals graze in designated strips. |
| Higher risk of overgrazing. | Lower risk of overgrazing. |
| Poor pasture utilization. | Better pasture utilization. |
Mob Grazing
Mob grazing involves moving large groups of animals frequently. This technique mimics natural grazing patterns. Animals graze intensely for short periods, then move to a new area. This allows the pasture to rest and recover.
Benefits of mob grazing include:
- Improved soil health: Trampling helps break down organic matter.
- Enhanced biodiversity: Different plants thrive.
- Better water retention: Soil structure improves.
Challenges of mob grazing:
- Labor-intensive: Frequent movement of animals.
- Requires planning: Need to monitor pasture conditions.
Forage Quality
Grazing management plays a vital role in ensuring the health and productivity of pastures. Proper grazing techniques can improve forage quality, animal health, and overall farm productivity. Forage quality directly impacts the nutritional intake of grazing animals, making it a key focus for farmers and ranchers.
Nutritional Value
Forage quality is closely tied to its nutritional value. High-quality forage provides essential nutrients for grazing animals. These nutrients include proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Animals need these nutrients to grow, reproduce, and stay healthy.
Several factors affect the nutritional value of forage:
- Plant species: Different plants offer different nutrient profiles.
- Growth stage: Younger plants tend to be more nutritious.
- Soil quality: Rich soil produces more nutritious forage.
- Weather conditions: Sunlight and rain can impact nutrient content.
A balanced diet is crucial for livestock health. Farmers must ensure their animals get enough protein, fiber, and energy. Here is a table showing the typical nutritional content of common forage types:
| Forage Type | Protein (%) | Fiber (%) | Energy (MJ/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alfalfa | 18-20 | 25-30 | 10-11 |
| Timothy Grass | 12-14 | 30-35 | 8-9 |
| Clover | 15-17 | 20-25 | 9-10 |
Farmers can use this information to plan their grazing schedules and ensure their animals receive optimal nutrition.
Seasonal Variation
Forage quality changes with the seasons. Spring and early summer are peak times for forage growth. During this period, plants are lush and full of nutrients. Animals grazing during these months get the best nutrition.
As the season progresses, forage quality can decline. Summer heat can cause plants to dry out and lose nutrients. By late summer and fall, forage quality may be at its lowest. Farmers need to plan for these changes to maintain animal health.
Here are some tips for managing seasonal variation in forage quality:
- Rotate grazing areas: Allow pastures to recover and grow new forage.
- Supplement diets: Provide additional feed during low-quality forage periods.
- Monitor weather: Adjust grazing plans based on weather conditions.
- Soil management: Use fertilizers to boost forage growth and quality.
Understanding seasonal variation helps farmers make informed decisions. By doing so, they ensure their animals receive consistent, high-quality nutrition year-round.
Animal Health
Grazing management plays a vital role in maintaining animal health. Proper grazing practices can lead to healthier livestock, better weight gain, and fewer diseases. This blog post will explore how effective grazing management can improve animal health, focusing on weight gain and disease prevention.
Weight Gain
Effective grazing management can significantly impact weight gain in livestock. Ensuring animals have access to high-quality forage is crucial. This provides them with the necessary nutrients for growth.
Rotational grazing is an excellent method. It allows pastures to rest and regrow. This ensures a continuous supply of fresh, nutritious grass. Here are some key benefits of rotational grazing:
- Improved forage quality - Fresh grass is more nutritious.
- Increased weight gain - Animals grow faster with better food.
- Better pasture health - Resting periods allow regrowth.
Supplementing grazing with additional feed can also help. This ensures animals receive all necessary nutrients. A balanced diet is essential for optimal weight gain.
Here is a simple table showing the benefits of supplementing grazing:
| Supplement | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Protein | Builds muscle mass |
| Minerals | Supports bone health |
| Vitamins | Boosts overall health |
Disease Prevention
Proper grazing management can significantly reduce the risk of diseases in livestock. Overgrazing can lead to poor pasture health and increased parasite load. Rotational grazing helps prevent this. It reduces the buildup of parasites in the soil.
Maintaining clean water sources is also crucial. Contaminated water can spread diseases quickly. Regularly check and clean water troughs to ensure they are safe for animal consumption.
Here are some tips for disease prevention through grazing management:
- Rotate pastures regularly - This helps break the life cycle of parasites.
- Provide clean water - This reduces the risk of waterborne diseases.
- Monitor animal health - Regular checks can catch diseases early.
Vaccination programs are also essential. They protect animals from common diseases. Work with a veterinarian to develop a suitable vaccination schedule.
These practices ensure healthier livestock. Healthy animals are more productive and can lead to higher profits for farmers.
Credit: www.zarebasystems.com
Environmental Considerations
Grazing management involves controlling how animals graze on pastures. This ensures sustainable use of land and resources. Environmental considerations are critical in grazing management. These help protect water resources and prevent soil erosion.
Water Resources
Protecting water resources is essential in grazing management. Water is vital for both animals and plants. Poor grazing practices can lead to water contamination. This affects the health of animals and the environment.
Here are some ways to protect water resources:
- Proper Fencing: Keep livestock away from water bodies to prevent contamination.
- Water Troughs: Use water troughs to provide clean water for animals.
- Riparian Buffers: Plant vegetation near streams and rivers to filter runoff.
Another effective method is rotational grazing. This involves moving livestock between different pasture sections. It prevents overgrazing and reduces soil compaction. This helps maintain healthy soil and clean water.
Monitoring water quality is also crucial. Regular checks ensure that water sources remain uncontaminated. This includes testing for pollutants and pathogens. Clean water supports healthy ecosystems and productive grazing lands.
Erosion Control
Erosion control is a key aspect of grazing management. Soil erosion can degrade land and reduce productivity. It also affects water quality by increasing sedimentation.
To control erosion, consider the following practices:
- Cover Crops: Plant cover crops to protect soil during off-seasons.
- Contour Farming: Farm along the natural contours of the land.
- Terracing: Create terraces on slopes to reduce runoff.
Grazing intensity should also be managed. Avoid overgrazing as it removes protective vegetation cover. This exposes soil to wind and water erosion. Balanced grazing helps maintain soil structure and health.
Another method is using erosion control structures. These include silt fences and check dams. They slow down water flow and capture sediment. This helps prevent soil loss and maintains land fertility.
Effective erosion control supports sustainable grazing. It ensures long-term productivity and environmental health. Implementing these practices benefits both farmers and the ecosystem.
Economic Factors
Grazing management is crucial for maintaining healthy pastures and livestock. Economic factors play a significant role in successful grazing practices. Understanding these factors can help farmers make informed decisions. This blog post will explore cost analysis and profitability strategies in grazing management.
Cost Analysis
Effective grazing management requires a thorough cost analysis. Farmers need to consider both fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs include land, fencing, and equipment. Variable costs cover feed, supplements, and labor.
A detailed cost analysis might include:
- Land expenses: Purchase or lease costs
- Fencing costs: Materials and installation
- Equipment costs: Purchase and maintenance
- Feed costs: Grazing supplements
- Labor costs: Wages for workers
Creating a budget helps in tracking all expenses. This ensures that no cost is overlooked. Farmers can use this data to identify areas where they can cut costs.
Here's a simple cost analysis table:
| Expense Type | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Land | $10,000 |
| Fencing | $2,000 |
| Equipment | $5,000 |
| Feed | $3,000 |
| Labor | $4,000 |
Profitability Strategies
Profitability in grazing management can be improved with smart strategies. Rotational grazing is one such strategy. This method involves moving livestock between pastures. It allows pastures to recover and grow back. This leads to better forage quality and quantity.
Other strategies include:
- Diversifying livestock: Raising different types of animals
- Improving pasture quality: Using fertilizers and reseeding
- Reducing feed costs: Growing own feed crops
- Efficient water management: Installing water troughs
- Monitoring livestock health: Regular check-ups and vaccinations
Smart planning can increase profitability. Farmers should keep detailed records of all activities. This helps in identifying the most profitable practices.
Investing in technology can also boost profits. Tools like drones and GPS systems can help monitor pastures. They provide valuable data for making informed decisions.

Credit: www.aces.edu
Technology In Grazing
Grazing management is crucial for maintaining healthy pastures and livestock. With the advent of technology, farmers can now monitor and manage their grazing systems more efficiently. This blog delves into the advanced tools and data management practices that are revolutionizing grazing management.
Monitoring Tools
Modern monitoring tools have made it easier to track livestock and pasture health. These tools include GPS collars, drones, and remote sensors. GPS collars help in tracking the movement of livestock. Farmers can see where their animals are grazing in real-time. This helps in making informed decisions.
Drones provide an aerial view of the pastures. They can detect overgrazing and areas that need attention. Remote sensors are used to monitor soil moisture and grass growth. These sensors send data to a central system. This ensures optimal grazing conditions.
- GPS Collars: Track livestock movement
- Drones: Aerial view of pastures
- Remote Sensors: Monitor soil and grass
Data Management
Effective data management is key to modern grazing systems. Data collected from various tools need to be analyzed. Software platforms help farmers in managing this data. These platforms store and analyze data from GPS collars, drones, and sensors.
Farmers can access this data through their smartphones or computers. This helps in making timely decisions. For instance, they can decide when to move livestock to a new area. They can also identify areas that need more attention.
| Tool | Data Collected |
|---|---|
| GPS Collars | Livestock Movement |
| Drones | Pasture Health |
| Remote Sensors | Soil and Grass Data |
Credit: extension.umn.edu
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Graze Management?
Graze management involves controlling livestock grazing to optimize pasture growth and animal health. It ensures sustainable land use and productivity.
What Is Managed Grazing?
Managed grazing is a livestock farming method. It involves rotating animals through pastures. This optimizes forage growth and soil health. The practice reduces erosion and improves biodiversity. It also enhances water retention and overall farm productivity. Managed grazing creates sustainable ecosystems.
What Is The Purpose Of Grazing?
Grazing helps manage vegetation, control weeds, and prevent wildfires. It supports biodiversity and enhances soil health. Livestock gain nutrients from grazing.
What Is The Effective Grazing Management?
Effective grazing management optimizes livestock health and pasture productivity. Rotational grazing, proper stocking rates, and rest periods for pastures are key. Monitor and adjust practices based on pasture conditions and livestock needs.
What Is Grazing Management?
Grazing management involves controlling livestock grazing to maintain pasture health and productivity.
Conclusion
Effective grazing management is essential for sustainable agriculture. Implement these strategies to improve pasture health and livestock productivity. Remember, consistent monitoring and adjustments are key. By optimizing your grazing practices, you contribute to a healthier environment and a thriving farm.
Start today and see the difference it makes in your grazing systems.
