The most common fertilizers in agriculture are nitrogen-based, phosphorus-based, and potassium-based. These nutrients are vital for plant growth and soil health.
Fertilizers play a crucial role in modern agriculture by enhancing soil fertility and boosting crop yields. Nitrogen-based fertilizers, like urea and ammonium nitrate, are essential for vegetative growth. Phosphorus-based fertilizers, such as superphosphate, promote root development and flowering. Potassium-based fertilizers, like potassium chloride, improve overall plant health and disease resistance.
Farmers carefully select these fertilizers based on soil tests and crop requirements. Proper fertilizer management ensures sustainable farming practices and minimizes environmental impact. By understanding the specific needs of their crops, farmers can achieve optimal production and contribute to global food security.
{getToc} $title={Table of Contents} $count={Boolean}
Macronutrient-based Fertilizers
Agriculture relies on fertilizers to boost plant growth and crop yields. Among the most common fertilizers used are macronutrient-based fertilizers. These fertilizers supply essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which plants need in large quantities. Let's delve into each type of macronutrient-based fertilizer and understand their importance in agriculture.
Nitrogen Fertilizers
Nitrogen is a critical nutrient for plant growth. It plays a key role in photosynthesis and helps plants produce vital proteins. Nitrogen fertilizers are widely used to ensure crops receive adequate nitrogen. There are several types of nitrogen fertilizers:
- Urea: Contains 46% nitrogen and is cost-effective.
- Ammonium Nitrate: Has 33-34% nitrogen and is highly efficient.
- Ammonium Sulfate: Contains 21% nitrogen and supplies sulfur.
- Calcium Nitrate: Provides nitrogen and calcium, beneficial for soil health.
Farmers often choose the type based on soil conditions and crop needs. Urea is popular for its high nitrogen content. Ammonium nitrate is valued for its quick-release properties. A table summarizing their features can help in decision-making:
| Type | Nitrogen Content | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Urea | 46% | Cost-effective |
| Ammonium Nitrate | 33-34% | Quick-release |
| Ammonium Sulfate | 21% | Supplies sulfur |
| Calcium Nitrate | 15% | Improves soil health |
Phosphorus Fertilizers
Phosphorus is vital for plant energy transfer and root development. Phosphorus fertilizers help in the early stages of plant growth. Common phosphorus fertilizers include:
- Single Superphosphate (SSP): Contains 16-20% phosphorus.
- Triple Superphosphate (TSP): Has 44-46% phosphorus.
- Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP): Contains 11% nitrogen and 48% phosphorus.
- Diammonium Phosphate (DAP): Has 18% nitrogen and 46% phosphorus.
Each type has specific advantages. SSP is good for general use. TSP is more concentrated, making it efficient for phosphorus-deficient soils. Here is a comparison table:
| Type | Phosphorus Content | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Single Superphosphate (SSP) | 16-20% | General use |
| Triple Superphosphate (TSP) | 44-46% | Concentrated |
| Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP) | 48% | Also provides nitrogen |
| Diammonium Phosphate (DAP) | 46% | Also provides nitrogen |
Potassium Fertilizers
Potassium is crucial for water regulation and enzyme activation in plants. Potassium fertilizers ensure that crops receive enough potassium, leading to stronger and more resilient plants. Common potassium fertilizers include:
- Potassium Chloride (Muriate of Potash): Contains 60-62% potassium.
- Potassium Sulfate (Sulfate of Potash): Has 50% potassium and supplies sulfur.
- Potassium Nitrate: Contains 44% potassium and also provides nitrogen.
- Potassium Magnesium Sulfate (K-Mag): Provides potassium, magnesium, and sulfur.
Potassium chloride is the most commonly used, but potassium sulfate is preferred for chloride-sensitive crops. Here's a table summarizing the benefits:
| Type | Potassium Content | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Potassium Chloride | 60-62% | High potassium content |
| Potassium Sulfate | 50% | Supplies sulfur |
| Potassium Nitrate | 44% | Also provides nitrogen |
| Potassium Magnesium Sulfate (K-Mag) | 22% | Supplies magnesium and sulfur |
Micronutrient-based Fertilizers
Fertilizers are vital in modern agriculture. They help plants grow strong and healthy. Among the many types of fertilizers, micronutrient-based fertilizers are essential for providing plants with the small amounts of nutrients they need to thrive. These nutrients are as crucial as the major ones, even though plants need them in smaller amounts. Let's dive into some common micronutrient-based fertilizers: Iron, Zinc, and Copper.
Iron Fertilizers
Iron is crucial for plants. It helps in photosynthesis and the formation of chlorophyll. Without enough iron, plants can become weak and pale. Iron fertilizers are used to supply this essential micronutrient.
Common forms of iron fertilizers include:
- Iron sulfate (FeSO4): This is a widely used form. It is effective but can be harsh on some plants.
- Iron chelates: These are more gentle and efficient. They are often used in soils with high pH levels.
Iron fertilizers can be applied in different ways:
- Soil application: Mixing with soil ensures that the roots can absorb the iron.
- Foliar spray: Spraying on the leaves is a quick way to correct iron deficiency.
Here is a table showing common iron fertilizers and their features:
| Type | Form | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Iron sulfate | Powder | Soil |
| Iron chelates | Liquid | Foliar/Soil |
Zinc Fertilizers
Zinc is another vital micronutrient. It supports enzyme function and protein synthesis. Without enough zinc, plants may show stunted growth and small leaves. Zinc fertilizers help to provide this key nutrient.
Common forms of zinc fertilizers include:
- Zinc sulfate (ZnSO4): This is the most common form. It is effective and widely used.
- Zinc oxide: This is another form, but it is less soluble than zinc sulfate.
Zinc fertilizers can be applied in different ways:
- Soil application: Ensures that the roots get the zinc they need.
- Foliar spray: Quick way to address zinc deficiency in plants.
Here is a table showing common zinc fertilizers and their features:
| Type | Form | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc sulfate | Powder | Soil |
| Zinc oxide | Powder | Soil |
Copper Fertilizers
Copper is important for photosynthesis and enzyme activity. Without enough copper, plants may show signs of chlorosis and poor growth. Copper fertilizers help to supply this essential micronutrient.
Common forms of copper fertilizers include:
- Copper sulfate (CuSO4): This is the most common form and is highly effective.
- Copper chelates: These are more gentle and efficient, often used in soils with high pH levels.
Copper fertilizers can be applied in different ways:
- Soil application: Ensures that the roots can absorb the copper.
- Foliar spray: Quick way to correct copper deficiency.
Here is a table showing common copper fertilizers and their features:
| Type | Form | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Copper sulfate | Powder | Soil |
| Copper chelates | Liquid | Foliar/Soil |
Organic Fertilizers
Farmers rely on fertilizers to boost crop growth and yield. Organic fertilizers are among the most popular choices in agriculture today. These fertilizers are made from natural materials like compost, manure, and bone meal. They offer numerous benefits to both plants and the environment.
Benefits Of Organic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers offer several advantages over synthetic ones. Here are some key benefits:
- Improves Soil Health: Organic fertilizers enhance the soil's structure, increasing its ability to hold water and nutrients.
- Environmentally Friendly: They are biodegradable and release fewer pollutants into the environment.
- Increases Microbial Activity: Organic matter in these fertilizers boosts the population of beneficial microbes in the soil.
- Slow Release of Nutrients: Organic fertilizers break down slowly, providing a steady supply of nutrients to plants.
- Reduces Chemical Usage: Using organic fertilizers decreases the need for chemical pesticides and herbicides.
Below is a table summarizing the main benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improves Soil Health | Enhances soil structure and water retention |
| Environmentally Friendly | Biodegradable and low pollution |
| Increases Microbial Activity | Boosts beneficial soil microbes |
| Slow Release of Nutrients | Provides steady nutrient supply |
| Reduces Chemical Usage | Less need for pesticides and herbicides |
Common Types Of Organic Fertilizers
Several types of organic fertilizers are used in agriculture. Here are some of the most common:
- Compost: Made from decomposed organic matter. It improves soil structure and adds nutrients.
- Manure: Animal waste that is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. It enriches soil fertility.
- Bone Meal: Ground animal bones. It is a great source of phosphorus and calcium for plants.
- Fish Emulsion: Liquid fertilizer made from fish waste. It provides a quick nutrient boost for plants.
- Green Manure: Plants grown specifically to be turned into the soil. They improve soil health and fertility.
Below is a table highlighting the common types of organic fertilizers:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Compost | Decomposed organic matter, improves soil structure |
| Manure | Animal waste, rich in essential nutrients |
| Bone Meal | Ground animal bones, provides phosphorus and calcium |
| Fish Emulsion | Liquid fertilizer from fish waste, quick nutrient boost |
| Green Manure | Plants grown to be turned into soil, improves soil health |
Using these organic fertilizers can make your farm more sustainable and productive.
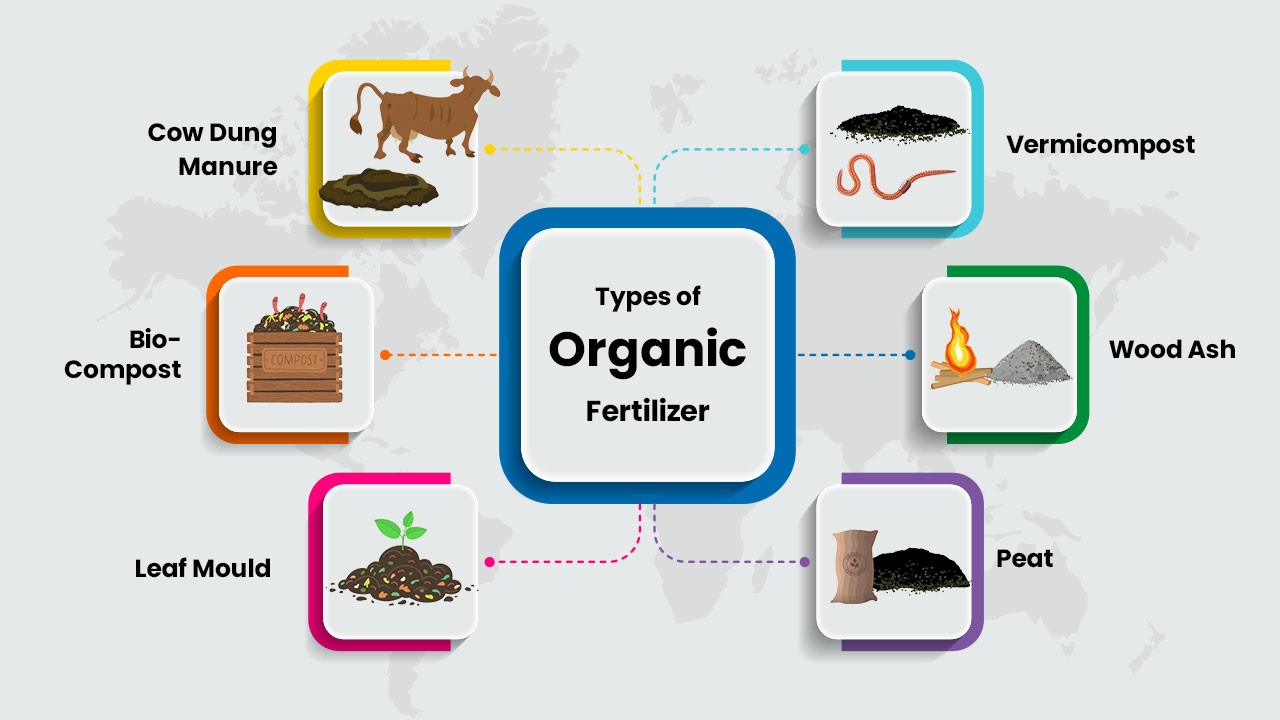
Credit: tractorguru.in
Synthetic Fertilizers
Fertilizers play a crucial role in modern agriculture. They provide essential nutrients that help crops grow faster and healthier. Among the various types of fertilizers, synthetic fertilizers are widely used due to their effectiveness. These fertilizers are man-made and contain chemicals that promote plant growth. They are an important tool for farmers who aim to increase crop yields and ensure food security.
Advantages Of Synthetic Fertilizers
Synthetic fertilizers offer several benefits that make them a popular choice among farmers. Here are some of the key advantages:
- High Nutrient Content: Synthetic fertilizers are rich in essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- Quick Results: These fertilizers are designed to release nutrients quickly, promoting rapid plant growth.
- Consistency: They offer a uniform nutrient composition, ensuring that all plants receive the same amount of nutrients.
- Cost-Effective: Synthetic fertilizers are often cheaper than organic options, making them more accessible to farmers.
- Easy to Apply: They come in various forms such as granules, powders, and liquids, making application simple and convenient.
In addition to these advantages, synthetic fertilizers are also available throughout the year. This ensures that farmers can use them whenever needed, without worrying about seasonal availability.
Disadvantages Of Synthetic Fertilizers
Despite their benefits, synthetic fertilizers also have some drawbacks:
- Environmental Impact: These fertilizers can cause soil pollution and water contamination if not used properly.
- Soil Degradation: Overuse can lead to soil degradation, reducing its fertility over time.
- Health Risks: The chemicals in synthetic fertilizers can pose health risks to humans and animals.
- Dependency: Continuous use can make crops dependent on these fertilizers, reducing soil's natural fertility.
Environmental concerns are particularly significant. Runoff from fields can carry these chemicals into rivers and lakes, harming aquatic life. This makes it crucial for farmers to use synthetic fertilizers responsibly.
Health risks are another critical issue. The chemicals can enter the food chain, potentially causing health problems for consumers. Therefore, it's essential to balance the use of synthetic fertilizers with organic options to minimize these risks.
Environmental Impact
Fertilizers play a crucial role in modern agriculture, helping to boost crop yields and ensure food security. However, the use of fertilizers comes with significant environmental implications. Understanding these impacts is essential for sustainable farming practices. This section will delve into the environmental impact of common fertilizers used in agriculture.
Effects Of Fertilizer Runoff
Fertilizer runoff occurs when excess fertilizers wash away from fields and enter water bodies. This process has several negative consequences:
- Water Pollution: Runoff introduces high levels of nitrogen and phosphorus into rivers, lakes, and oceans. These nutrients can cause algae blooms, which deplete oxygen levels and harm aquatic life.
- Soil Degradation: Excessive fertilizer use can lead to soil acidification and nutrient imbalances. This affects soil health and reduces its ability to support crops.
- Impact on Human Health: Contaminated water sources can lead to health problems for humans. Nitrates in drinking water can cause conditions like methemoglobinemia, or "blue baby syndrome."
Below is a table summarizing the effects of fertilizer runoff:
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Water Pollution | Algae blooms, reduced oxygen levels, harm to aquatic life |
| Soil Degradation | Acidification, nutrient imbalances, reduced soil health |
| Human Health | Nitrate contamination, health conditions like methemoglobinemia |
Sustainable Fertilizer Practices
Sustainable fertilizer practices aim to minimize environmental harm while maintaining crop productivity. Here are some effective strategies:
- Precision Farming: This involves using technology to apply fertilizers more accurately. It reduces waste and ensures nutrients are delivered where needed most.
- Organic Fertilizers: Organic options like compost and manure release nutrients slowly. They improve soil structure and reduce the risk of runoff.
- Crop Rotation: Rotating crops can help maintain soil health and reduce the need for chemical fertilizers. Different crops use and replenish different nutrients.
Using these practices helps farmers achieve better yields while protecting the environment. Below is a quick comparison of conventional and sustainable fertilizer practices:
| Practice | Conventional | Sustainable |
|---|---|---|
| Application Method | Broadcast spreading | Precision application |
| Type of Fertilizer | Chemical | Organic |
| Soil Health | Often degraded | Improved |
Implementing sustainable practices is vital for the future of agriculture and the planet.
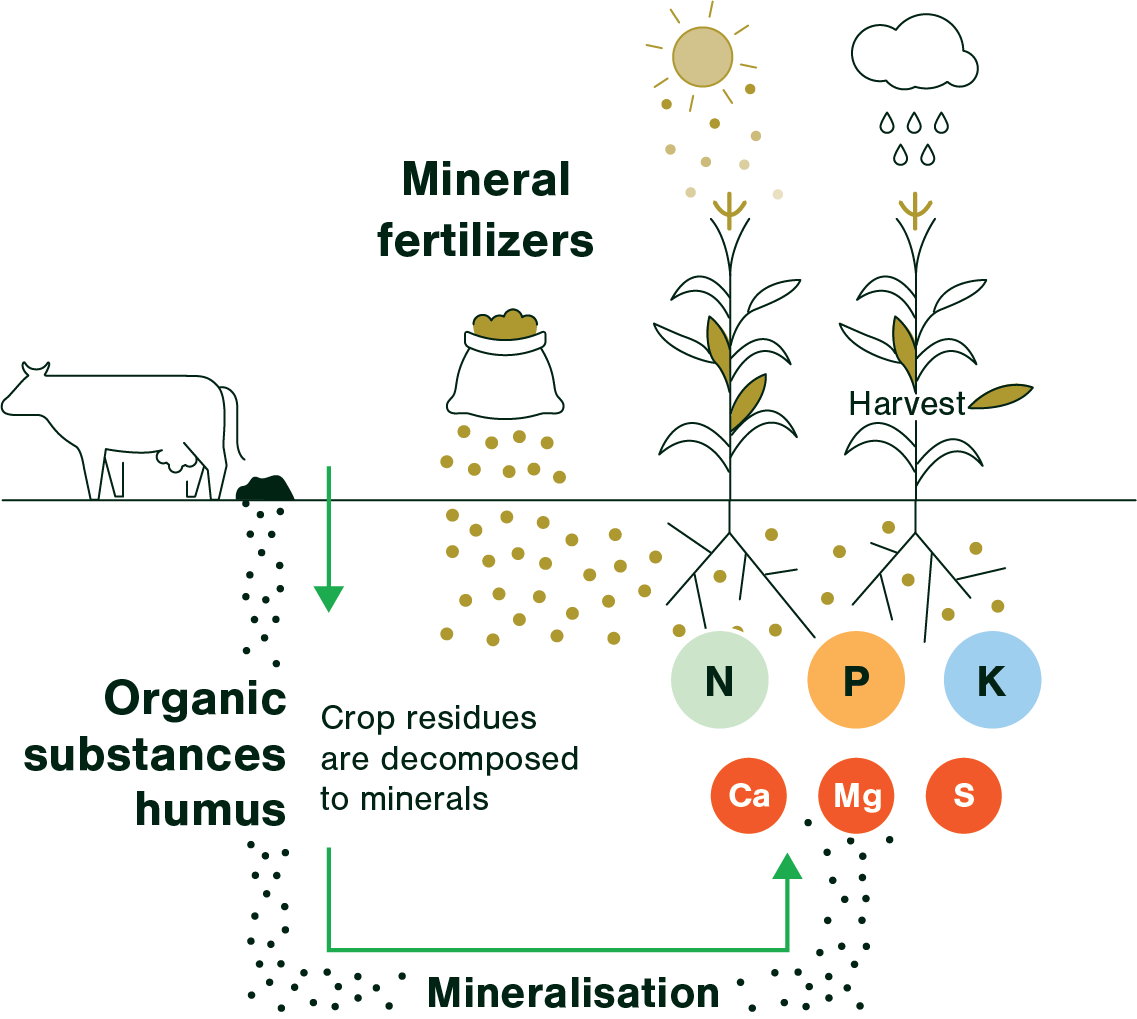
Credit: www.fertilizerseurope.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Top 3 Fertilizers?
The top 3 fertilizers are Miracle-Gro, Osmocote, and Jobe's Organics. Miracle-Gro provides balanced nutrients. Osmocote offers slow-release nutrition. Jobe's Organics boosts soil health.
What Is The Most Widely Used Fertilizer?
The most widely used fertilizer is urea. It provides essential nitrogen to plants, promoting growth and increasing crop yields.
What 3 Fertilizers Are Most Important For Crops?
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are the three most important fertilizers for crops. They promote growth, root development, and overall plant health.
Which Fertilizer Is Best For Agriculture?
The best fertilizer for agriculture depends on the crop and soil type. Organic fertilizers like compost and manure improve soil health. Chemical fertilizers like NPK provide essential nutrients quickly. Always test soil before choosing.
What Are The Main Types Of Fertilizers?
The main types are organic, inorganic, and biofertilizers.
Conclusion
Farmers benefit greatly from using common fertilizers. They improve soil health and boost crop yields efficiently. Choosing the right fertilizer ensures sustainable agriculture practices. Understanding these fertilizers helps farmers make informed decisions. This knowledge leads to better productivity and environmental sustainability.
Start implementing these fertilizers for a thriving agricultural future.

