Cattle breeding involves selecting and mating cattle to improve desired traits. It enhances livestock productivity and genetic quality.
Cattle breeding is a crucial agricultural practice that focuses on improving livestock characteristics. Farmers select cattle based on traits like milk production, growth rate, and disease resistance. This selective breeding ensures healthier and more productive herds. Advanced techniques like artificial insemination and genetic testing further refine the process.
{getToc} $title={Table of Contents} $count={Boolean}
Sustainable cattle breeding practices can boost farm profitability and food security. By focusing on genetic improvement, farmers can meet market demands and adapt to changing environmental conditions. Cattle breeding, therefore, plays a significant role in modern agriculture, ensuring a robust and efficient livestock industry.
The Importance Of Cattle Breeding
Cattle breeding is a crucial part of farming. It helps farmers improve the quality and productivity of their herds. Breeding can lead to better milk production, stronger animals, and healthier offspring. This blog post will discuss various aspects of cattle breeding.
Genetic Improvement
Genetic improvement allows farmers to choose the best traits for their cattle. Traits like disease resistance and high milk yield are very important. Selective breeding can help create stronger generations over time.
Increased Productivity
Breeding can greatly increase productivity on farms. Cows that produce more milk can help a farm earn more money. Farmers can breed cows that grow faster and weigh more. This helps in getting more meat and milk from each animal.
Better Disease Resistance
Healthy cattle are essential for a successful farm. Breeding can help reduce the chances of disease. Farmers can choose animals with strong immune systems. This helps to create herds that are less likely to get sick.
Enhanced Animal Welfare
Good breeding practices can improve animal welfare. Cattle with better health and stronger bodies live happier lives. Farmers can breed cows that are more adapted to their environment. This ensures that the animals are comfortable and healthy.
Economic Benefits
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Higher Profits | Cows that produce more milk and meat help farms earn more money. |
| Reduced Costs | Healthier cows need less medical care, saving farmers money. |
| Improved Efficiency | Better breeding practices lead to more efficient farming operations. |
Sustainable Farming
Cattle breeding supports sustainable farming practices. Efficient breeding reduces the need for excessive resources. Farmers can focus on creating stronger and healthier herds. This helps in maintaining the environment and supporting long-term farming goals.
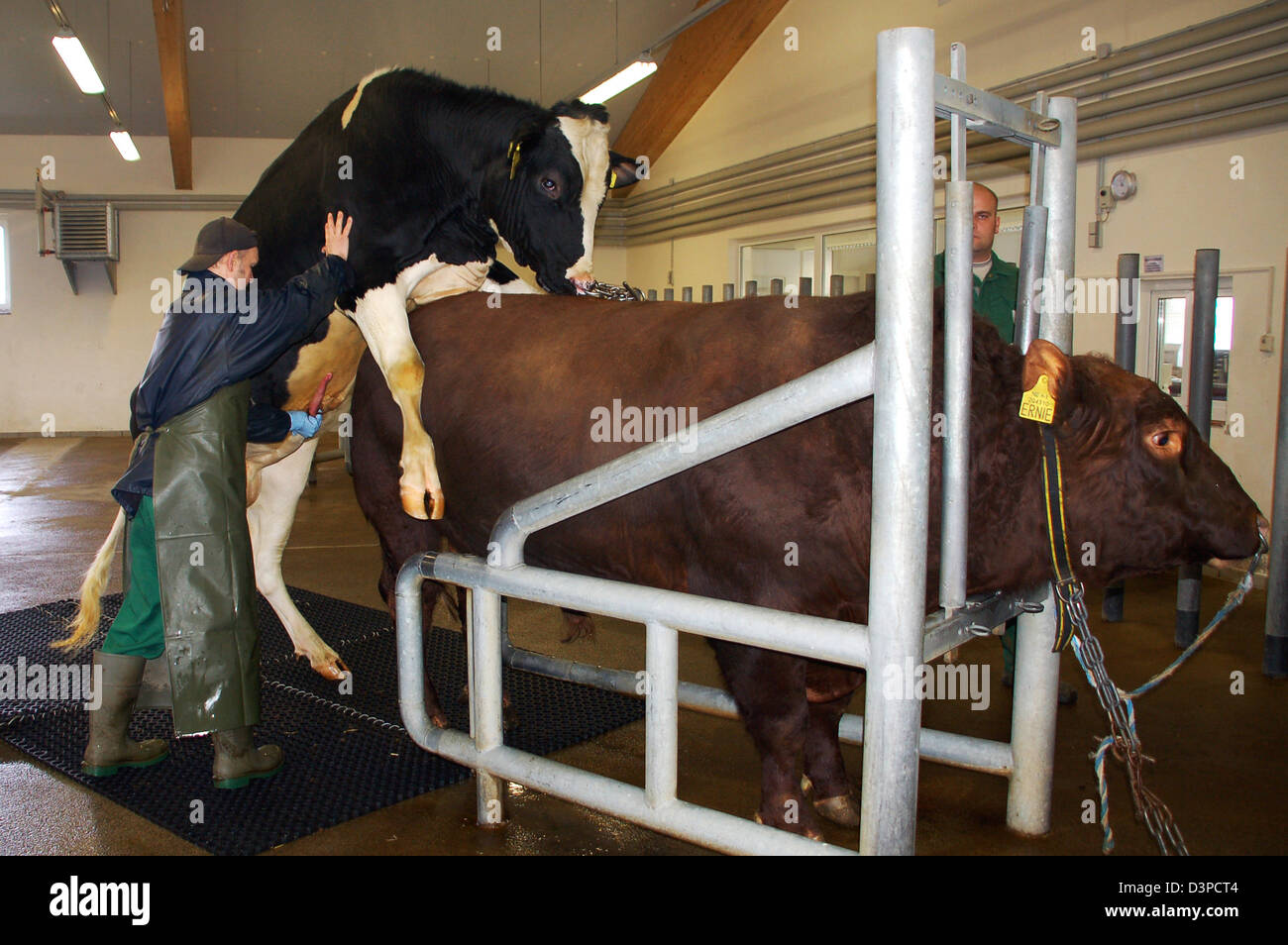

Credit: www.alamy.com
Factors To Consider In Cattle Breeding
Cattle breeding is a crucial aspect of livestock management that requires careful consideration of various factors. The primary aim is to improve the quality and productivity of cattle. This blog post will discuss the key factors to consider in cattle breeding, including genetics, health, temperament, and productivity. Understanding these elements can help farmers make informed decisions to enhance their herds.
Genetics
Genetics play a significant role in cattle breeding. Choosing the right genes can improve the herd's quality and productivity. Select cattle with strong genetic traits for desirable characteristics.
- Disease resistance - Choose cattle with a history of good health.
- Growth rate - Opt for breeds that grow quickly and efficiently.
- Milk production - Select cows that have high milk yield.
- Meat quality - Choose breeds known for tender and flavorful meat.
Using genetic testing can help identify the best candidates. This ensures that only the best genes are passed on to the next generation. Breeding programs should focus on maintaining genetic diversity. This helps in preventing inbreeding and associated problems.
Health
The health of cattle is essential for successful breeding. Healthy cattle produce healthier offspring. Regular health checks are crucial.
- Vaccination - Ensure all cattle are vaccinated against common diseases.
- Nutrition - Provide a balanced diet to meet their nutritional needs.
- Parasite control - Implement regular deworming and parasite control measures.
- Veterinary care - Schedule regular visits from a veterinarian.
Maintaining a clean and safe environment is also important. This reduces the risk of disease and injury. Stress-free cattle are healthier and more productive. Provide ample space, clean water, and comfortable living conditions.
Temperament
Temperament is another important factor in cattle breeding. Cattle with a calm disposition are easier to manage. They are less likely to cause injuries to themselves or handlers.
- Docility - Choose cattle that are easy to handle and less aggressive.
- Mothering ability - Select cows that are good mothers and protect their calves.
Observing cattle in different situations can help assess their temperament. Handling them gently can also improve their behavior over time. Training and positive reinforcement are effective methods to manage cattle temperament. This ensures a safer and more productive environment for both cattle and farmers.
Productivity
Productivity is a key goal in cattle breeding. High productivity means better returns on investment. Focus on cattle that excel in their specific roles.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Milk Yield | Cows that produce more milk are more valuable. |
| Growth Rate | Cattle that grow quickly reach market weight sooner. |
| Reproductive Efficiency | Cows that calve regularly and without issues. |
| Meat Quality | Breeds known for tender and flavorful meat. |
Keeping detailed records of each cow's performance can help identify top performers. This information is vital for making breeding decisions. Selective breeding can improve productivity over generations. Farmers should continually evaluate and adjust their breeding strategies to achieve the best results.
Breeding Techniques
Cattle breeding is an important part of farming. Farmers use it to improve their herds. Breeding techniques help to get better cattle. This means healthier cows and more milk. It also means more beef. There are three main techniques. These are natural breeding, artificial insemination, and embryo transfer. Each technique has its own advantages and challenges.
Natural Breeding
Natural breeding is the most traditional way to breed cattle. It involves a bull and a cow. The bull mates with the cow in a natural way. This method has been used for thousands of years. It is simple and does not need special tools.
There are some benefits of natural breeding:
- Low cost: No special equipment needed.
- Natural process: Mimics how animals breed in the wild.
- Less labor: Farmers do not need to do much.
Natural breeding has some drawbacks too. One is that it can spread diseases. Another is that it is hard to control. Farmers cannot pick the best bull and cow easily. This can lead to less healthy calves. Farmers must take care of bulls, which can be dangerous.
Artificial Insemination
Artificial insemination is a modern technique. It involves placing sperm into a cow's uterus. This is done without a bull. A farmer or vet uses special tools. This method has many benefits. It is very popular among farmers today.
Some benefits of artificial insemination include:
- Controlled breeding: Farmers can choose the best bulls.
- Prevents diseases: No contact between bulls and cows.
- Cost-effective: One bull's sperm can breed many cows.
There are some challenges too. It requires special tools and training. Farmers need to store sperm properly. This can be costly. Timing is very important. Farmers must know when cows are ready to breed. This method needs more work and planning.
Embryo Transfer
Embryo transfer is an advanced breeding technique. It involves transferring embryos from one cow to another. The first cow, called the donor, provides the embryo. The second cow, called the recipient, carries the embryo to birth. This method has some unique advantages.
Some benefits of embryo transfer include:
- High-quality calves: Combines the best traits of two cows.
- Increased breeding rate: One donor cow can produce many calves.
- Disease control: Embryos are screened for diseases.
Embryo transfer also has some challenges. It is very expensive. It needs special skills and equipment. This method is complex and requires careful planning. Farmers must monitor both donor and recipient cows closely. It is not suitable for all farms due to high costs and complexity.
Breeding Programs
Cattle breeding is a critical practice in the agricultural industry. It involves selecting the best animals to reproduce, enhancing their desirable traits, and ensuring a healthy herd. Breeding programs are essential for improving productivity, health, and quality in cattle. These programs can include various methods, such as selective breeding, crossbreeding, and inbreeding. Understanding these methods is crucial for farmers to make informed decisions and achieve their breeding goals.
Selective Breeding
Selective breeding is a method where farmers choose the best animals to reproduce. This method focuses on enhancing specific traits like milk production, meat quality, or disease resistance. Farmers carefully select cattle based on their genetic qualities and performance. The main steps in selective breeding include:
- Identifying desirable traits
- Choosing the best-performing animals
- Pairing selected animals for reproduction
A detailed record-keeping system is essential for tracking the performance of the cattle. Farmers often use pedigree charts to trace the genetic history of their herd. This helps in making informed decisions about which animals to breed. Selective breeding can lead to significant improvements in the herd's overall quality and productivity.
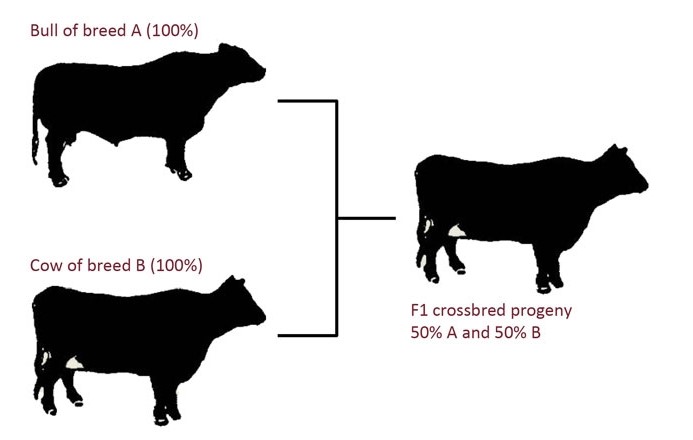
Crossbreeding
Crossbreeding involves mating animals from different breeds. The goal is to combine the best traits from each breed to produce superior offspring. This method can result in improved growth rates, better disease resistance, and higher fertility. Some common benefits of crossbreeding include:
- Increased genetic diversity
- Improved vigor and health
- Enhanced production traits
Farmers often use a systematic approach to crossbreeding, selecting breeds that complement each other. For example, one breed may be known for its high milk production, while another may excel in disease resistance. By combining these traits, farmers can create a more robust and productive herd. Crossbreeding also helps reduce the risk of genetic disorders that can occur in purebred animals.
Inbreeding
Inbreeding involves mating closely related animals, such as siblings or parent-offspring pairs. This method aims to preserve specific traits within a herd. While it can help maintain genetic consistency, it also has risks. Some potential issues with inbreeding include:
- Increased risk of genetic disorders
- Reduced fertility
- Weaker immune systems
Farmers need to carefully monitor their herds when using inbreeding. It's crucial to balance the benefits and risks. Inbreeding can be useful for fixing certain traits, but it should be done with caution. A diverse gene pool is essential for maintaining a healthy and productive herd. Proper management and regular health checks are vital to mitigate the risks associated with inbreeding.
Improving Cattle Genetics
Cattle breeding involves choosing the best animals to reproduce. This improves their traits. Improving cattle genetics is crucial. It helps in producing healthier and more productive cattle. This post explores three methods: genetic testing, genetic selection, and genetic engineering.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing helps identify the best cattle for breeding. It involves analyzing DNA. This reveals important traits. Farmers can check for diseases. They can also see traits like milk production and growth rate.
- Early detection of diseases
- Better trait selection
- Higher productivity
- Collect DNA samples from cattle.
- Send samples to a lab.
- Analyze the DNA.
- Review the results.
- Decide which cattle to breed.
Genetic Selection
Genetic selection involves choosing cattle with the best traits to breed. This improves the herd over generations. Farmers look at records. They consider traits like milk yield, growth rate, and disease resistance.
- Pedigree selection: Choosing based on family history.
- Performance testing: Selecting based on individual performance.
- Progeny testing: Evaluating offspring performance.
- Improved traits over time
- Healthier cattle
- Higher productivity
Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering involves directly modifying cattle DNA. This creates cattle with desired traits. Scientists can add or remove specific genes. This technique is more precise.
- Disease resistance: Adding genes to fight diseases.
- Improved milk production: Modifying genes for higher yield.
- Faster growth: Enhancing growth rate genes.
- Identify the target gene.
- Use tools to modify the DNA.
- Introduce the modified gene into cattle.
- Monitor the cattle for desired traits.
- Precise trait improvement
- Faster results
- Healthier and more productive cattle
Common Breeds Of Cattle
Cattle breeding is an essential part of farming. Different breeds have unique traits. Some are good for milk, while others are best for meat. This guide explores the common breeds of cattle.
Holstein
Holstein cattle are the most popular dairy breed. They are known for producing a lot of milk. Their black and white spots make them easy to recognize. Farmers love them because they are gentle and easy to handle.
Angus
Angus cattle are famous for their beef. They have black coats and are very hardy. Their meat is known for being tender and tasty. Angus cattle are also easy to raise and very adaptable to different climates.
Hereford
Hereford cattle have a distinct red coat with white faces. They are very good for beef production. These cattle are known for their calm nature and easy-going temperament. They also have great grazing ability, making them a favorite among farmers.
Jersey
Jersey cattle are small but very productive. They are famous for their rich and creamy milk. Their milk has high butterfat content. Jerseys are easy to manage and are very friendly.
Brahman
Brahman cattle are known for their resilience. They can handle hot climates very well. Their unique hump and large ears help them stay cool. These cattle are often used in crossbreeding to improve other breeds.
Challenges In Cattle Breeding
Cattle breeding is a vital component of the agricultural industry. It involves the selection and mating of cattle to produce desired traits. Breeders face numerous challenges that can affect the efficiency and success of their breeding programs. Understanding and overcoming these challenges is crucial for sustainable cattle breeding.
Disease Control
Disease control is one of the major challenges in cattle breeding. Diseases can spread quickly among cattle, leading to significant losses. Effective management practices are essential to prevent and control diseases.
Common diseases that affect cattle include:
- Foot and Mouth Disease
- Bovine Tuberculosis
- Brucellosis
Preventive measures include:
- Regular vaccination
- Quarantine of new animals
- Maintaining hygiene in cattle sheds
Early detection and treatment of diseases can help minimize losses. Regular health check-ups and monitoring are crucial for maintaining cattle health.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in cattle breeding. Climate conditions can directly impact cattle health and productivity. Extreme weather conditions can cause stress and reduce fertility rates.
Key environmental factors include:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Availability of water and feed
Adaptation strategies are important to mitigate the impact of environmental factors. These strategies include:
- Providing shade and shelter
- Ensuring adequate water supply
- Feeding a balanced diet
Monitoring environmental conditions and making necessary adjustments can help maintain cattle health and improve breeding outcomes.
Market Demand
Market demand significantly influences cattle breeding. Understanding market trends is crucial for breeders to make informed decisions. Breeders need to produce cattle that meet market requirements.
Factors affecting market demand include:
- Consumer preferences
- Price fluctuations
- Economic conditions
Strategies to meet market demand include:
- Selecting breeds with desirable traits
- Improving meat quality
- Enhancing milk production
Keeping up with market trends and adjusting breeding programs accordingly can help breeders meet market demands effectively.
Credit: futurebeef.com.au

Credit: www.farmprogress.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Best Breeding Method For Cattle?
The best breeding method for cattle is artificial insemination. It ensures genetic diversity, improves herd quality, and increases productivity.
How Many Times Will A Bull Breed A Cow In Heat?
A bull typically breeds a cow in heat multiple times, usually around 2 to 4 times within her 12-18 hour heat period.
How Fast Do Cattle Reproduce?
Cattle typically reproduce once a year. A cow's gestation period lasts about 9 months. Calves are usually weaned at 6-8 months.
How Many Times Can You Breed A Cow?
A cow can typically be bred until around 8-10 years old. This usually allows for 6-8 calves in her lifetime.
What Is Cattle Breeding?
Cattle breeding is the process of selecting and mating cattle to enhance desirable traits in future generations.
Conclusion
Cattle breeding plays a crucial role in ensuring sustainable livestock farming. By implementing best practices, farmers can improve herd health and productivity. Investing in quality genetics and proper management techniques will yield long-term benefits. Embrace modern breeding methods to optimize cattle performance and secure a prosperous future for your farm.
